|
UV LIGHT:
UV light is the electromagnetic energy at wavelengths
between X-rays and visible light. The electromagnetic spectrum is illustrated
below.
Electromagnetic Spectrum
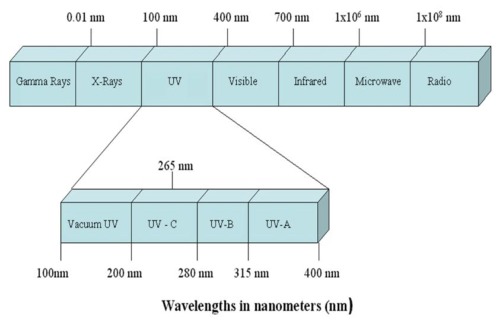
UV light is broken down into three regions: UV-A, UV-B,
and UV-C. UV-A consists of wavelengths from 315 – 400 nm. These
are the wavelengths that cause skin to tan. UV-B consists of wavelengths
from 280 – 315 nm. These are the wavelengths that cause sunburn.
UV-C consists of wavelengths from 100 – 280 nm. These are the
wavelengths of interest in water disinfection because they damage DNA
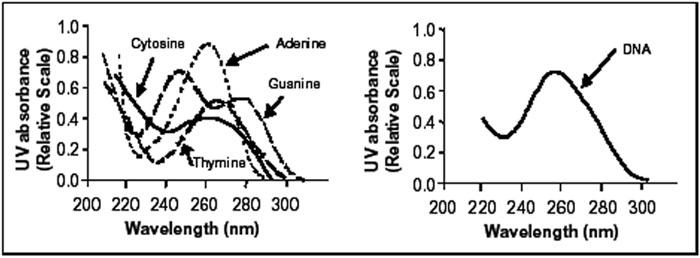
and RNA in cells. The germicidal range is where DNA absorbance is the
highest, 240 – 290 nm with the peak at 265 nm. The figure below
illustrates the DNA absorbance spectra.
UV Absorbance of Nucleotides and Nucleic Acid
at pH 7 (USEPA, 2003)
This germicidal UV does not immediately inactivate the
organism but introduces genetic interference that inhibits replication
of the organism.
Key measurements assessing the amount of light absorbed by the transmitting
medium (e.g. water) are UV absorbance and UV transmittance. The UV absorbance
is determined by the following equation:
A = log10(Io
/ It) = log10(1 / T)
Where:
A = absorbance
Io = initial UV intensity
It = measured UV intensity at receptor
The percent transmittance is determined by the following equation:
%T = (It / Io) X 100%
or %T = 10-A
Where T = percent transmittance
|